Locating places on Earth means using common reference points (cardinal directions, globes, maps, imaginary lines) to know where continents, countries and cities are. In 5th grade geography, students first learn to use the cardinal directions (north, south, east, west) and different representations of the Earth (globe, world maps). Then they discover important imaginary lines such as the Equator, the hemispheres, some lines of latitude and longitude that form a grid to locate any place more precisely. You can go back to the homepage by clicking here! You can find the French lesson here.
Locating Places on Earth – 5th Grade Geography
Different ways to represent Earth
The Earth is round: it has a spherical shape. We can see oceans and continents on its surface. Because it is mostly covered by oceans and seas, the Earth is often called the « blue planet ». We can represent the Earth in different ways:
Satellite photographs
| Satellite photographs are pictures taken from space by satellites. They show the real appearance of the Earth, but we can only see part of the planet at a time. |

The globe
| A globe is a model of the Earth in the shape of a sphere. It shows the true shapes of the continents and oceans, but we cannot see everything at once. More than 500 years ago, Magellan’s ships left Europe and sailed west. After three years, they came back to their starting point. This journey showed that the Earth is round. |

The world map (planisphere)
| A world map is a flat representation of the Earth. It lets us see the whole world at once, but the continents are distorted. The most common map projection used in schools is the Mercator projection. |
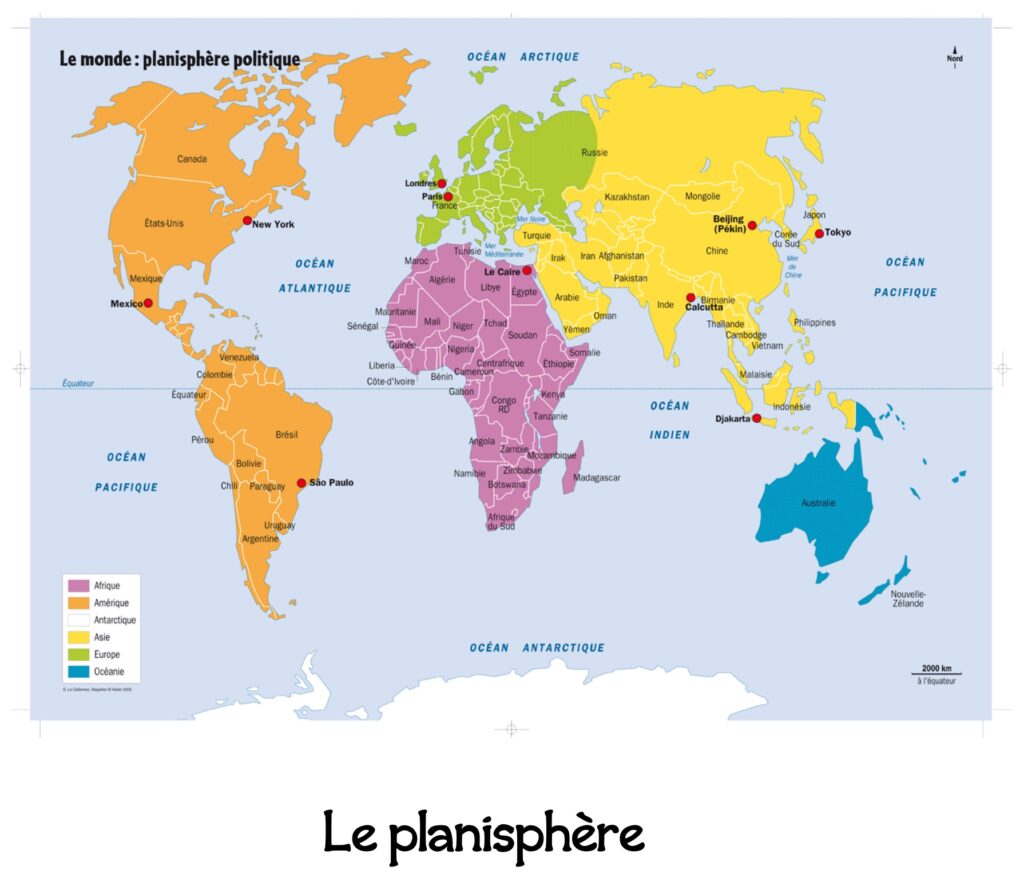
How do we locate places on Earth?
To locate places on Earth, we use reference points and imaginary lines drawn on globes and maps.
Cardinal directions
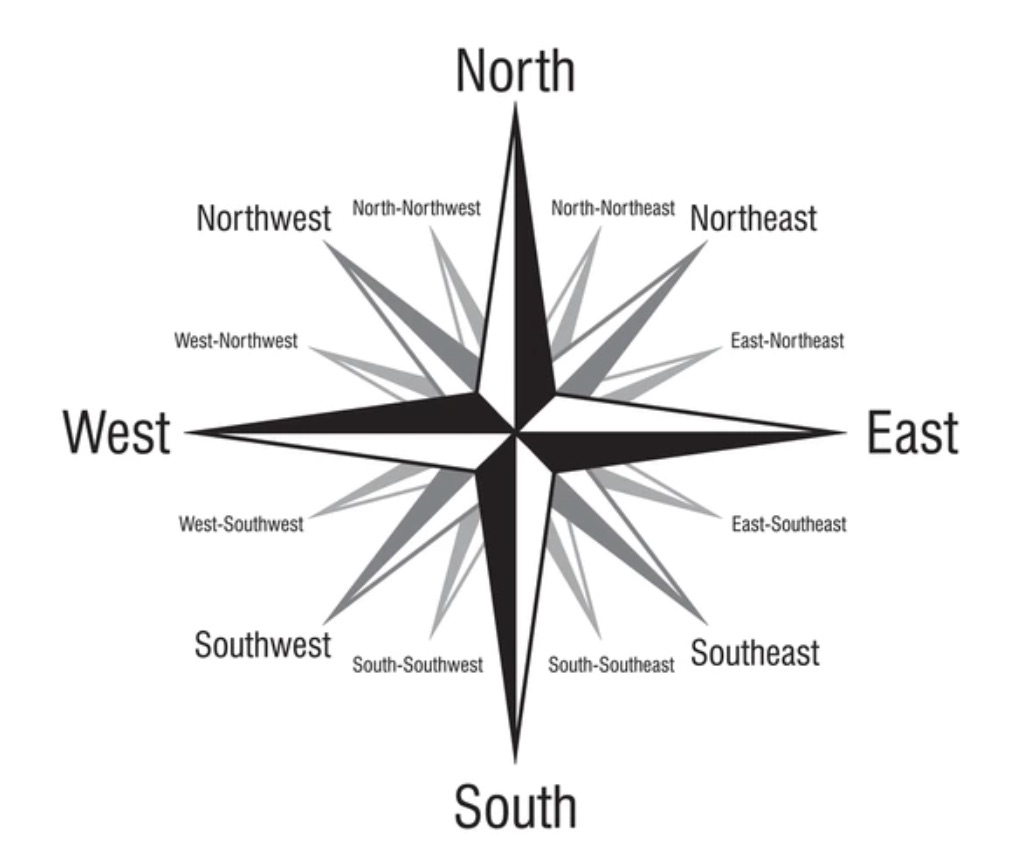
Reference points and imaginary lines
Parallels and Meridians
To move around the Earth, geographers, scientists, and travelers need to know precisely how to locate themselves on our planet.
The Parallels
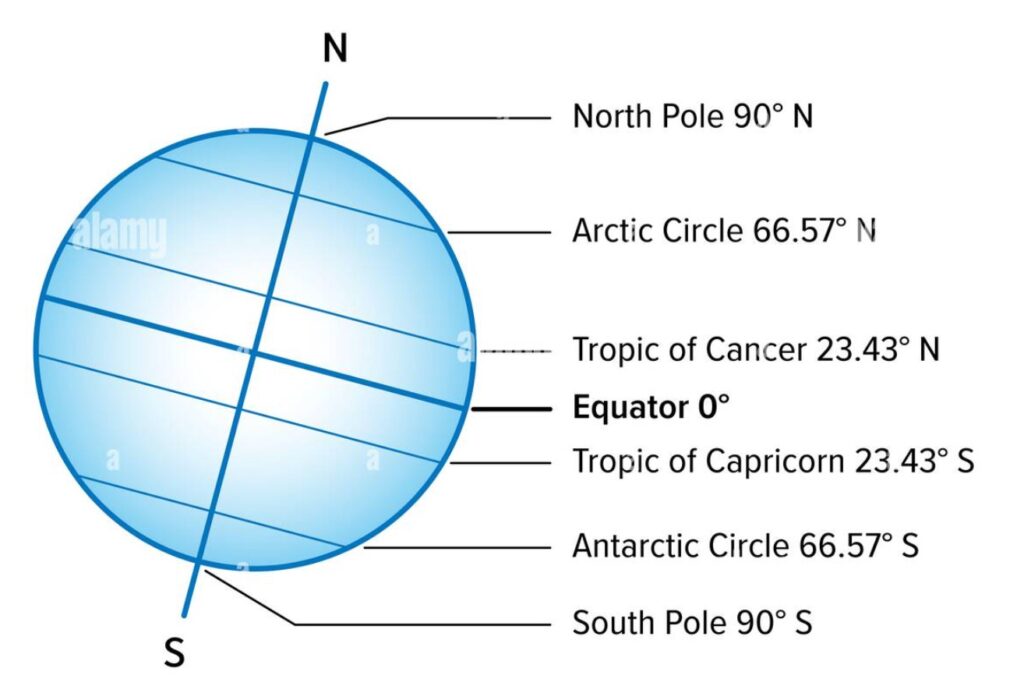
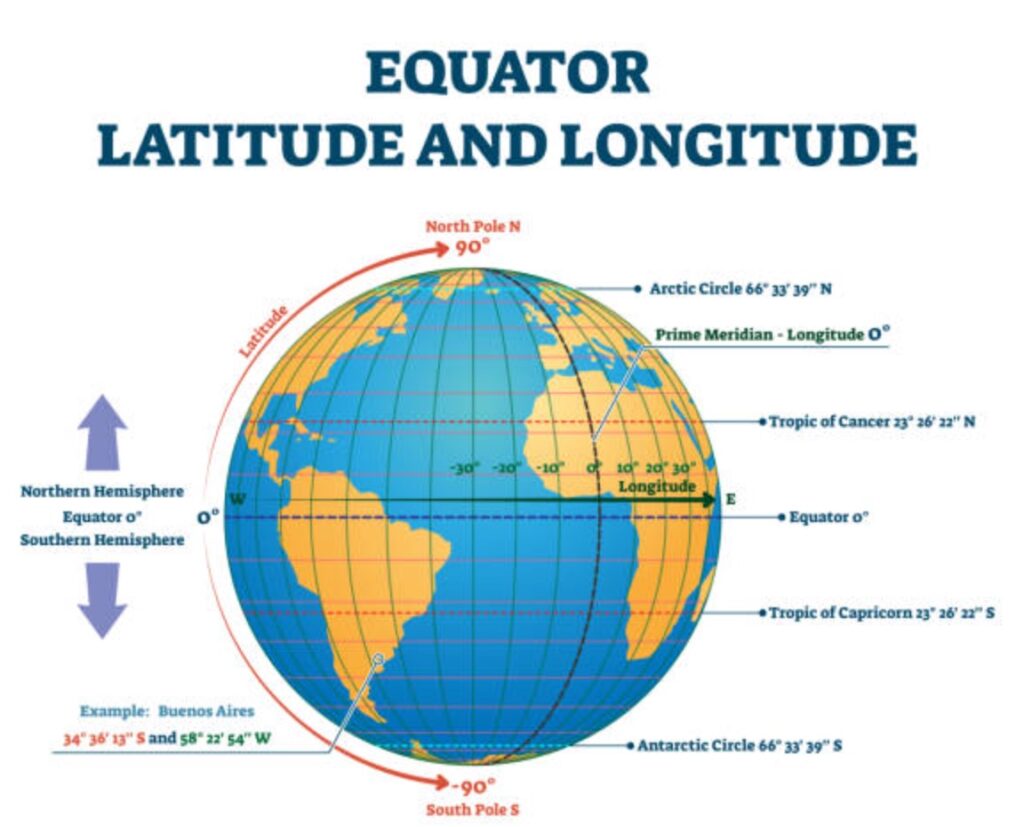
The Equator is an imaginary line that divides the Earth into two equal parts called hemispheres. It forms a circle around the globe. When we draw lines parallel to the Equator, we get the parallels.
Each parallel forms a circle around the Earth. The parallels indicate latitude — that is, the distance from the Equator. The Equator is at zero degrees latitude. The parallels are numbered from 0° to 90° toward the North and from 0° to 90° toward the South.
The Meridians
The Earth rotates around a slightly tilted axis that passes through the poles. The meridians are half-circles that connect the North Pole and the South Pole. They are used to measure longitude. The reference meridian (at zero degrees) is the Greenwich Meridian, located near London in the United Kingdom. The meridians are numbered from 0° to 180° eastward and from 0° to 180° westward.
When the parallels and the meridians cross, they form a grid that helps locate any place on Earth. With this grid, every point can be identified by giving its latitude (North or South) and its longitude (West or East).
Quiz – Finding Your Way on Earth: Parallels, Meridians, Equator, Tropics (Grades 4–5)
1. What is the Equator?
2. What do we call the two halves of the Earth separated by the Equator?
3. What is a parallel?
4. What is a meridian?
5. What is the name of the meridian chosen as the origin (0° longitude)?
6. The Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn are:
7. Where is the Tropic of Cancer?
8. Where is the Tropic of Capricorn?
9. What are parallels and meridians used for on maps and globes?
10. Which sentence is true?
Skills – Locating Places on Earth (5th Grade)
| Skill: locating places on Earth | Indicator of success |
|---|---|
| Name the main parts of the Earth | The student can name continents and oceans on a world map. |
| Use cardinal directions | The student correctly uses north, south, east and west to describe the position of a place on a map or globe. |
| Locate places on a world map | The student locates simple reference points (Equator, poles, hemispheres) and can tell in which hemisphere a continent or country is located. |
| Understand imaginary lines | The student explains that the Equator, parallels and meridians are imaginary lines used to locate places on Earth. |
| Read maps at different scales | The student locates the same place on a town map, a regional map, a country map and a world map, and understands the idea of scale. |
